Varicose veins commonly occur during pregnancy, affecting approximately half of all pregnant women. These enlarged and dilated veins, typically found in the legs, can cause discomfort and aesthetic concerns. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and management of varicose veins in pregnancy, providing you with valuable insights and tips to navigate this common pregnancy complication.
Understanding Varicose Veins
Varicose veins occur when the valves in the superficial veins of the legs become weak or damaged, leading to blood pooling and increased pressure. During pregnancy, hormonal changes and increased blood volume place additional strain on the circulatory system, contributing to the development of varicose veins. The growing uterus also exerts pressure on the pelvic veins, impeding blood flow and exacerbating the condition.
While varicose veins are often hereditary, certain factors can increase the likelihood of their occurrence during pregnancy. These include a family history of varicose veins, excessive weight gain, and hormonal fluctuations. It is important to note that varicose veins are typically temporary conditions that improve after childbirth, but they may worsen with subsequent pregnancies.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Varicose veins in pregnancy can manifest with various symptoms, including:
- Aching, throbbing, or heavy sensation in the legs
- Swelling in the feet and ankles
- Itchiness around the affected veins
- Leg cramps
- Discoloration of the skin
- Development of hemorrhoids in the rectal area
While varicose veins are generally harmless, it is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider if you experience severe pain, skin ulceration, or signs of venous insufficiency, such as skin breakdown or blood clots.

Preventing Varicose Veins in Pregnancy
Although it may not be possible to completely prevent varicose veins during pregnancy, adopting certain preventive measures can help minimize their impact. Consider the following tips:
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: As approved by your healthcare provider, engage in regular exerciseto promote circulation and strengthen leg muscles. A balanced diet rich in fiber and hydration can also contribute to overall vascular health.
- Avoid Prolonged Sitting or Standing: Take breaks and avoid long periods of immobility, as this can impede blood flow and contribute to the development of varicose veins. When sitting, elevate your legs or use a footrest to reduce pressure on the veins.
- Elevate Your Legs: Whenever possible, elevate your legs above heart level to encourage blood flow back to the heart. Prop your legs on pillows or use a reclining chair for optimal elevation.
- Wear Compression Stockings: Compression stockings provide external support to the veins, helping to improve circulation and reduce swelling. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate level of compression and the best time to wear them.
- Sleep on Your Left Side: Sleeping on your left side reduces pressure on the inferior vena cava, the large vein responsible for returning blood from the lower body to the heart. This position facilitates blood flow and can alleviate the burden on your circulatory system.
Managing Varicose Veins During Pregnancy
While varicose veins typically resolve on their own after childbirth, there are several self-care measures you can take to manage the symptoms and promote comfort during pregnancy. Consider the following strategies:
- Regular Exercise: Engage in low-impact exercises, such as walking or swimming, to improve circulation and strengthen leg muscles. Avoid high-impact activities that may strain the veins.
- Avoid Tight Clothing: Opt for loose-fitting clothing that does not constrict blood flow. Tight garments can exacerbate the symptoms of varicose veins and impede circulation.
- Cooling Measures: Apply cool compresses or use ice packs wrapped in a cloth to reduce swelling and alleviate discomfort. Ensure that the cold temperature is not directly applied to the skin.
- Hydration and Nutrition: Maintain adequate hydration by drinking plenty of water throughout the day. Additionally, consume a diet rich in fiber to prevent constipation, which can contribute to the development of hemorrhoids.
- Proper Leg Positioning: Avoid crossing your legs while sitting, as this restricts blood flow. Instead, keep your legs uncrossed and elevate them when possible.

Seeking Medical Intervention
In most cases, varicose veins in pregnancy do not require medical intervention and improve spontaneously after delivery. However, if your symptoms persist or worsen, or if you experience complications such as skin ulceration or blood clots, consult with your healthcare provider. They may recommend the following treatment options:
- Prescription Grade Compression Stockings: Your healthcare provider may prescribe compression stockings with a higher level of compression to alleviate swelling and discomfort.
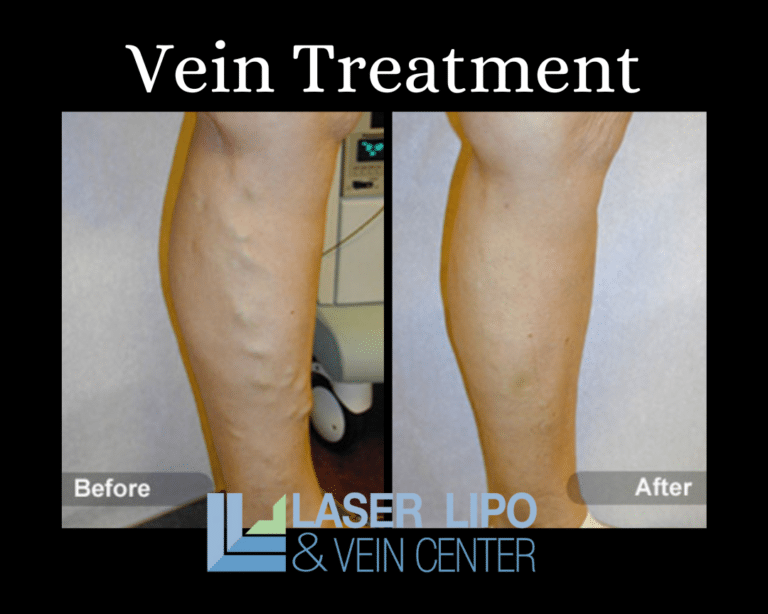
- Sclerotherapy: This minimally invasive procedure involves injecting a solution directly into the affected veins, causing them to shrink and gradually fade away. Sclerotherapy is typically safe during pregnancy but should be discussed with your healthcare provider.
- Surgery: In rare cases where conservative measures prove ineffective or complications arise, surgical interventions such as vein ligation, vein stripping, or phlebectomy may be considered. These procedures involve the removal or closure of the affected veins.
It is essential to discuss the potential risks and benefits of any medical intervention with your healthcare provider, as the safety and appropriateness of certain treatments may vary during pregnancy.
Conclusion
Varicose veins are a common occurrence during pregnancy, resulting from hormonal changes, increased blood volume, and the pressure exerted by the growing uterus. While they are generally harmless and resolve after childbirth, they can cause discomfort and aesthetic concerns. By adopting preventive measures, managing symptoms through self-care, and seeking medical guidance when necessary, you can navigate the journey of pregnancy with greater ease and comfort. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and support throughout your pregnancy.