What Is Lymphedema?
Lymphedema occurs when a clear fluid known as lymphatic fluid builds up and causes fluid retention in the soft tissues of your body. Usually, this occurs in the arms and legs. The lymphatic system consists of lymph vessels and lymph nodes. Lymph vessels collect a fluid that is made up of water, fats, protein, and wastes from the cells of the body. Furthermore, lymph vessels carry this fluid to your lymph nodes. After that, lymph nodes filter waste materials and then recycle the fluid to your blood. However, damaged or missing vessels and nodes cause the lymph fluid blockage. In this case, they are unable to cycle through your system. In addition, the fluids can create localized fluid retention and cause swelling, known as lymphedema. This usually affects the arms or legs.
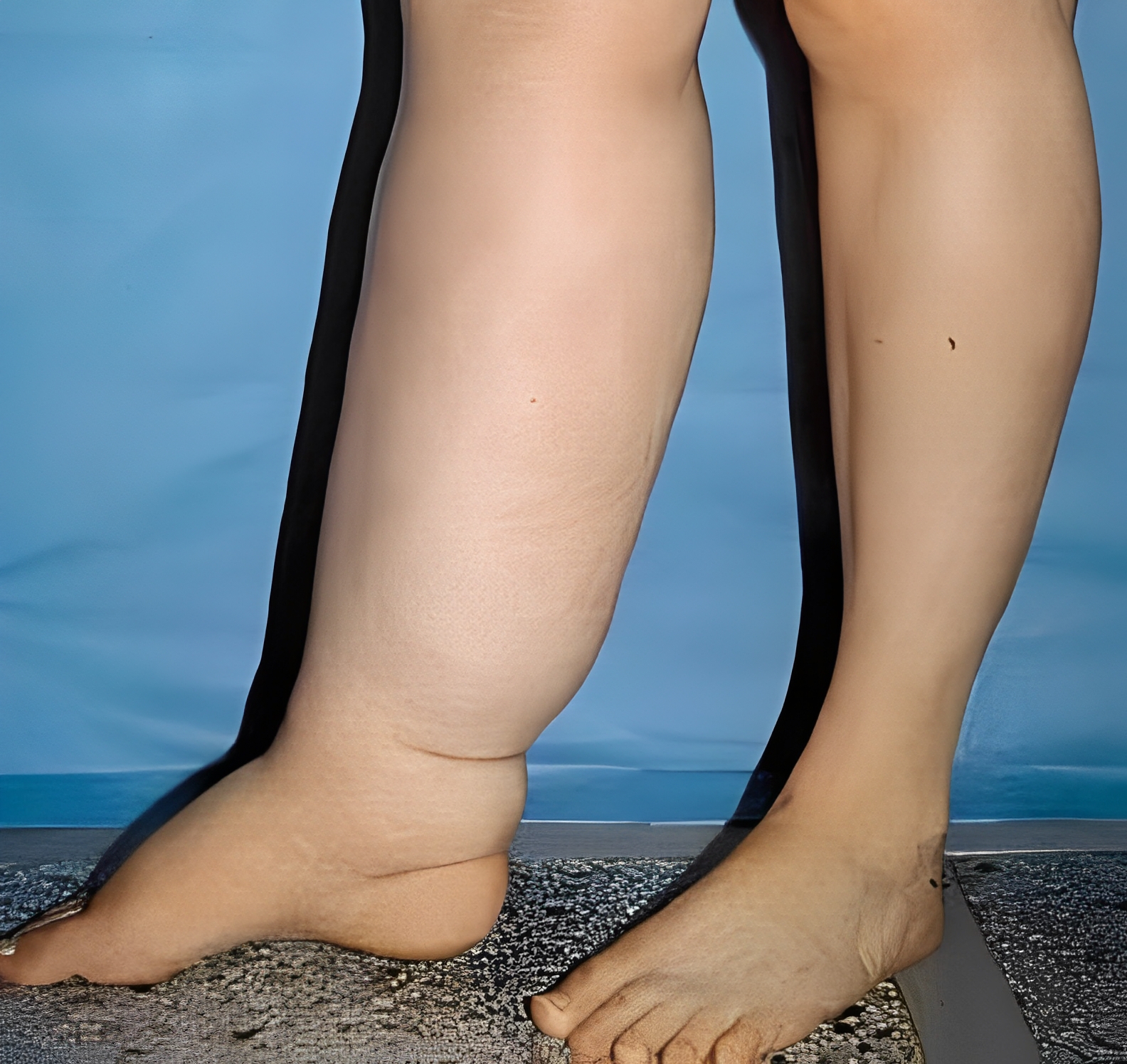
Furthermore, injuries to your lymphatic system, also known as secondary lymphedema, can cause lymphedema. This is actually the most common form of lymphedema. Unfortunately, people can develop chronic lymphedema, which can last for the rest of their lives. In addition, chronic lymphedema can be difficult to treat with lymphedema therapy and it increases the likely hood to contract an infection. Minor injuries to the skin can cause lymphangitis. For example, a cut, scratch, insect bite, or athlete’s foot can create a severe infection if you don’t treat it promptly. Moreover, lymphangitis affects the connective tissue under the skin. Additionally, multiple infections can cause scarring that makes the tissue vulnerable to more swelling and infection. On top of that, advanced chronic lymphedema can lead to fibrosis or hardening of the tissue.
What Are the Symptoms of Lymphedema?
In short, symptoms do not always occur immediately. They can sometimes occur 15 or more years following an injury to your lymphatic system. When symptoms eventually occur, they can include:
- Aching, weakness, redness, heaviness, or tightness in one of your limbs
- Less flexibility in your wrist or ankle
- Tight-fitting rings or shoes
What Causes Lymphedema?
Infection is the most common cause of lymphedema to the legs. The second most common cause is an injury. Additionally, other causes of lymphedema to the legs are from cancer and hereditary conditions.
What Tests Will I Need?
You will first need a general health check from your physician regarding medical history and symptoms before finding a lymphedema specialist. After that, you will need a physical exam. Also, your physician may measure your affected limbs.
In order to confirm a lymphedema diagnosis, your physician may order tests, including one or more of the following:
- Lymphoscintigraphy, which uses a low-dose injected radioactive substance to trace the flow of lymph fluid through your lymphatic vessels.
- A duplex ultrasound, which uses high-frequency sound waves and Doppler technology to show vessels and real-time blood flow on a screen, often necessary to rule out a blood clot in your leg.
- Lymphangiography, which uses contrast (dye) directly injected into the lymphatic vessels. This is now used less frequently.
Lymphedema Therapy & Treatment
Most importantly, you can prevent lymphedema even if you know you are at risk without the need for lymphedema treatment surgery. Initially, if you have mild lymphedema, you can take measures to prevent it from worsening. The following precautions can minimize symptoms:
Clean your affected limb regularly. With that said, remember to dry it thoroughly and apply lotion:
- If you shave the affected area, use an electric razor
- Don’t go barefoot
- Do not cross your legs when you sit
- Do not carry a handbag with your affected arm
- Compression wraps and stockings
On top of that, manual lymphatic drainage can be beneficial. Other treatments for lymphedema include special exercises that you can do while wearing compression stockings or bandages. You can also use external pumps to aid the movement of fluid through your body. In short, complex decongestive therapy is a combination of these exercises which is followed by a lifestyle change.
Unfortunately, medication cannot cure lymphedema or provide any concrete lymphedema therapy but it may treat associated conditions. Therefore, antibiotics can help in combating infections that can worsen lymphedema symptoms.
Your St. Louis Lymphedema Doctor is A Call Away
Call our lymphedema specialist today at (314) 627-0755.