It’s not uncommon for individuals suffering from underlying vein disease or venous insufficiencies to ignore the signs and symptoms of an issue until physical symptoms being to show up. While the evidence of a health risk may lie below the surface of the skin, veins play an integral role in overall well-being, and maintaining high standards of vein health is important is reducing the risk of more serious conditions such as Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT).
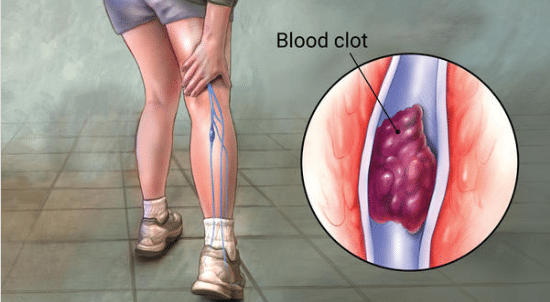
What Is DVT?
DVT directly interferes with the essential cardiovascular system and occurs when blood doesn’t successfully move back and forth between the heart and body’s extremities. In a healthy body, arteries carry oxygen-full blood away from the heart and out to replenish the body. Veins are then charged with carrying oxygen-depleted blood back to the heart for recirculation. DVT occurs when a blood clot blocks blood in the veins from successfully being returned to the heart for oxygen replenishment and distribution. While blood clots generally occur in the lower extremities and thighs, they also have the potential to develop in other veins throughout the body.
When the blood in the veins is blocked, it quickly begins to flow backward in the wrong direction away from the heart and starts to pool in the extremities. This pooling effect is often associated with painful swelling in the limbs. This can cause immediate issues in the affected limb, but disrupted blood flow ultimately affects the health of the entire body including the heart and potentially the lungs over time. In the event a clot breaks free and travels to the lungs, it can cause a pulmonary embolism which often proves to be fatal.
Because it’s estimated that anywhere from 300,00 to 600,000 Americans are affected by DVT annually, understanding the risk factors can help individuals to take the necessary steps to reduce the potential for developing this dangerous condition.
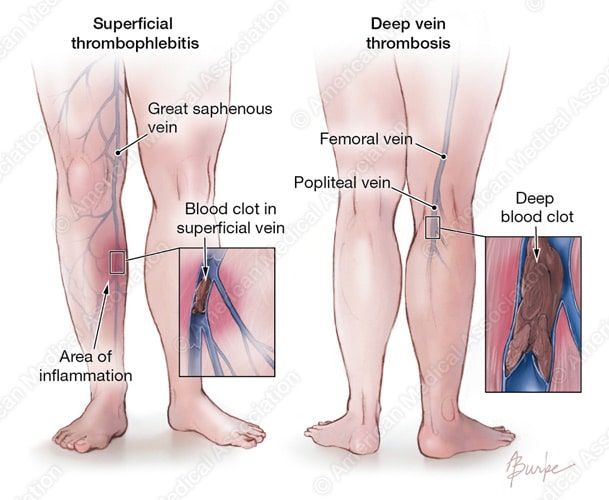
Risk Factors to Consider
Currently, physicians are able to point to a vast number of potential risk factors when it comes to the development of DVT in patients. While symptoms of DVT may be fairly similar and might include swelling and discoloration of the skin, the causes behind the symptoms may stem from a myriad of scenarios.
Lifestyle Affects the Risk Factor
Some physicians find that individuals who are prone to extended periods of sitting due to their work or lifestyle are more susceptible to the development of DVT. This may involve extended timeframes spent flying or driving or those individuals who are confined to bed rest. Healthy blood circulation throughout the body depends on leg muscles contracting regularly. In these situations, muscles are still for long periods of time and clots can begin to form when blood isn’t regularly stimulated to circulate through these extremities.
Obesity is another lifestyle condition often pointed to as a primary culprit in the development of DVT. Individuals who are significantly overweight often struggle with venous insufficiencies as added weight puts added pressure on veins. This can interrupt healthy circulation and lead to potential blood clots over time. Smoking is another lifestyle habit that has the potential to increase the overall risk of DVT as it can directly affect healthy circulation leading to clotting.
Genetic Links
While lifestyle choices play a significant role when looking at risk for DVT, sometimes the condition is simply inherited through genetics. Many individuals suffer from blood disorders that allow for blood to clot more easily and those with a family history of DVT or cancer-causing genetic predispositions may find themselves in a category of individuals more prone to DVT in the long-term.
Linked Conditions
Many physicians have found that the risk of DVT increases in partnership with other conditions an individual may present with. Those individuals suffering from inflammatory bowel disease may be at an increased risk for developing DVT. Similarly, those suffering from heart failure are particularly at risk as overall blood circulation is hindered throughout the body. Those individuals that are already fitted with a pacemaker or vein catheters may increase their DVT risk as blood flow is decreased and the walls of blood vessels are more prone to irritation. Additionally, those who have recently had surgery or suffered from previous venous injuries often seen disruptions in overall circulation which increases the risk for developing DVT with time.
Hormonal Fluctuations
During pregnancy, women often experience increased pressure on the legs and pelvis which frequently increases the risk of DVT. This risk remains rather high for up to 6 weeks following the delivery of the baby. Those women undergoing hormone replacement therapy or those that regularly use birth control pills are also more susceptible to the development of clots over time. In general, individuals over the age of 60 are at a naturally increased risk for developing DVT.
Contact Our Clinic Today
When you’re looking for a place to establish important vein health care or have questions regarding DVT, be sure to contact Dr. Wright and his team at the St. Louis Laser Vein Center today. We’re committed to providing comprehensive patient care and can’t wait to partner with you on your journey to healthy living.